Winer JB Guillain Barré syndrome Mol Pathol 01 Dec 54(6)3815 Ye Y, Zhu D, Wang K, Wu J, Feng J, Ma D, et al Clinical and electrophysiological features of the 07 GuillainBarré Abstract The clinical picture of GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is heterogeneous and involves the classical demyelinating type of inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP), the more rapid and usually less benign motor or motorsensory axonal forms (AMAN, AMSAN), and the antiGQ1b spectrum of Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS) Paraparetic GuillainBarre syndrome is an uncommon variant of GBS We describe a case of a teenage boy, who developed progressive, symmetric weakness of the lower limbs following an upper respiratory tract infection CSF findings, electrodiagnostic testing and ruling out focal lesions by neuroimaging There was also a history of an

Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning
What is guillain barre syndrome csf
What is guillain barre syndrome csf- Additional truncal dysesthesia prompted spinal cord MRI with unremarkable findings Lumbar CSF on day 2 after onset of neurological symptoms showed normal cell counts (2/mm 3) and protein level (64 mg/dl) and a serum/CSF glucose ratio of 0 Due to the history of pulmonary symptoms a chest‐computed tomography was performed and revealedSural sparing is a common phenomenon when testing sensory nerves CSF analysis commonly shows an elevated protein, but this elevation may not be present until the third week of the illness Patients with AIDP are treated with best medical management and either IV immunoglobulin (IVIg) or plasma exchange Summary GBS is a common form of acute quadriparesis;



Cureus Neurological Complications Of Covid 19 Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Pfizer Covid 19 Vaccine
Guillain Barre Syndrome MFS could be confused with a brainstem lesion, such as an infarct or encephalitis, and this has raised the theory that Miller Fisher is a brainstem disease CSF findings in miller fisher syndrome and bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis MFS and BBE were described in the 1950s, and similarities to GBS were indicatedLocal clinical care facilities and treatment options may also influence the clinical course and outcome of GuillainBarré syndrome CSF examination may be useful in cases of clinical uncertainty about the diagnosis, especially to exclude other causes associated with CSF pleocytosis, such as infectious polyradiculitis and acute poliomyelitis (Guillain et al, 1916) In all 455 patients whereIn the course of the GuillainBarré syndrome with autonomic dysfunction the changes in hemodynamic indices suggest a state of sympathetic hyperactivity There is
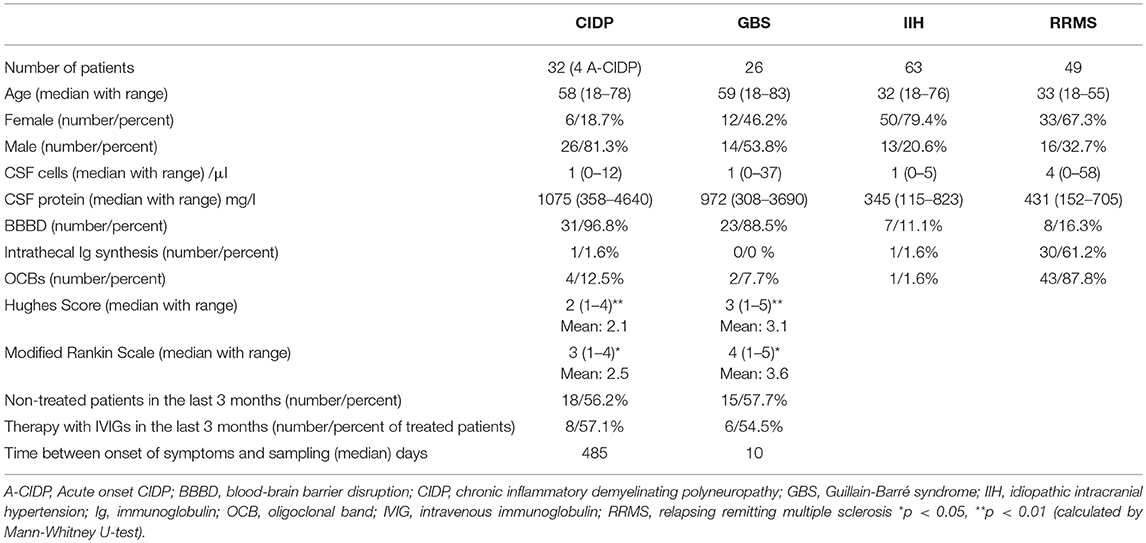
Central nervous system complications are reported in an increasing number of patients with Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID19) COVID19–related GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is of particular importance given its association with higher Decreased myotatic reflexes Complete areflexibsent reflexes Peaks within four weeks peaks by two weeks in 50 percent of Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) refers to a group of acute, autoimmune polyneuropathies Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (AIDP) This is the most common cause of GBS (8590% of patients) The pathophysiology involves demyelination Patients often can recover relatively rapidly (over several weeks to months) Axonal Variants
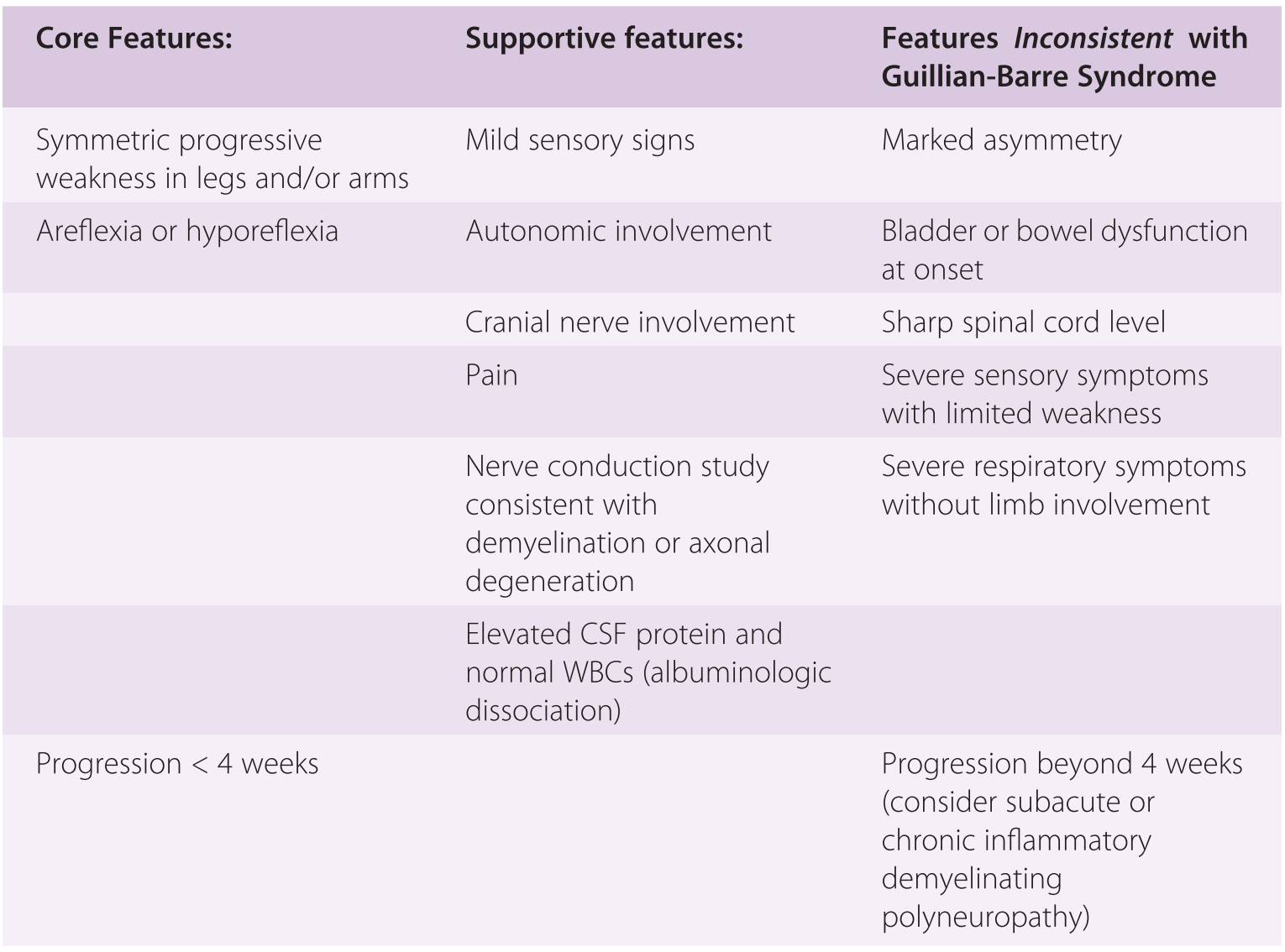
Abstract GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an acute, immunemediated, postinfectious polyneuropathy with symmetrical ascending weakness, diminished deep tendon reflexes, and nonspecific sensory symptoms CSF protein is raised with normal or Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS), or acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, is characterized by ascending motor paresis peaking within 4 weeks, diminished or absent muscle stretch reflexes, sensory symptoms with minimal objective sensory loss, electrophysiologic evidence of a demyelinating neuropathy, and CSF albuminocytologic dissociation1 Variants of this syndrome CSF findings in paraproteinemic neuropathies canomad and poems The protein concentration was mildly elevated in the CSF of 68% of 16 patients with CANOMAD (05–1 g/L), while lymphocytic pleiocytosis (7–16 cells/μL) was observed only in 3 cases, and oligoclonal bands were absent ( Willison et al, 01 )




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Jev Infection Nejm




The Guillain Barre Syndrome And Multiple Sclerosis In Vitro Cellular Responses To Nervous Tissue Antigens Nejm
Guillain Barre Syndrome MFS is one of several GuillainBarré variants, which include a pure sensory variant, a pure dysautonomic variant, and a purely motor variant, and some patients have motor and sensory variants CSF findings in miller fisher syndrome and bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis GuillainBarré syndrome, or acute Background Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) and Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS) are emerging as known consequences of COVID19 infection CSF findings or outcome between these groups Intubation wasThe first week of disease course the CSF may be normal, but thereafter from second week onward, there is an elevation in CSF protein in almost 90% of cases25 Transient oligoclonal bands and increased myelin basic protein may be detected in the CSF of few GBS patients7 Electrodiagnostic features of nerve conduction are




Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein In Guillain Barre Syndrome Need For Age Dependent Interpretation Hegen 21 European Journal Of Neurology Wiley Online Library




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician
ASFSN, acute small fibre sensory neuropathy; At variance with CSF findings, we found a discrepancy concerning MRI findings between classic GBS and COVID19related GBS Specifically, while most cases of the former group showed typically spinal root enhancement at MRI , in the latter group, in analogy with Zikaassociated GBS, the same finding was less frequently reported 84Common initial symptoms were distal dysaesthesias (51% vs 71%) and gait disturbance (49% vs 35%) At disease onset, 19% of the Romberg signnegative patients complained of diplopia, and during the illness 49%, but there were no signs of external opthalmoplegia




Clinical Significance Of Serum And Csf Findings In The Guillain Barre Syndrome And Related Disorders Semantic Scholar




Pertinent Laboratory Findings For Each Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Download Scientific Diagram
GuillainBarre Syndrome (GBS) is mostly described as a postinfectious phenomenon and its occurrence during acute phase of illness is of interest GBS has recently been reported during the active phase of COVID19 for the first timeGuillainBarré syndrome is a relatively common, acute, and rapidly progressive, inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy The diagnosis is usually established on the basis of symptoms and signs, aided by cerebrospinal fluid findings and electrophysiologic criteria patients with GuillainBarré syndrome die Neurologic problems persist in up to percent of patients with the disease, and onehalf of these patients are severely disabled




Rheumatic Presentations Of Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Diagnostic Challenge A Case Series Sciencedirect




Clinical Features And Prognosis With Guillain Barre Syndrome
SSR, sympathetic skin response; Diagnostics of the GuillainBarré Syndrome Detecting the GuillainBarré Syndrome The diagnostic algorithm consists of anamnesis (1–3 weeks previous respiratory infection, gastrointestinal infection), fitting clinical findings (quickly ascending flaccid paralysis), exclusion of differential diagnoses, and additional diagnostics The following tests andGuillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapidonset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain often in the back along with muscle weakness, beginning in the feet and hands, often spreading to the arms and upper body



Guillain Barre Syndrome In 2 Patients With Covid 19 The Egyptian Journal Of Neurology Psychiatry And Neurosurgery Full Text



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
Recently, the Brighton Collaboration developed a new set of case definitions for GuillainBarré syndrome, again in response to a possible association between GuillainBarré syndrome and the H1N1GuillainBarre syndrome will have no history of any of these events, and the diagnosis should be made independent of them In IIB, which deals with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) findings in GBS, 10 or fewer mononuclear leukocytes per cubic millimeter is the expected finding, but 11 to 50 mononuclear leukocytes per cubic millimeter maySpinal fluid Characteristic findings in Guillain–Barré syndrome are an elevated protein level, usually greater than 055 g/L, and fewer than 10 white blood cells per cubic millimeter of fluid ("albuminocytological dissociation") Considering this, what virus causes Guillain Barre Syndrome?




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Zika Virus Infection In Colombia Nejm



Frontiers Immune Cell Profiling Of The Cerebrospinal Fluid Provides Pathogenetic Insights Into Inflammatory Neuropathies Immunology
GuillainBarré syndrome has typically been defined to be an illness characterised by progressive and symmetric motor weakness of more than one limb with areflexia 1 However, several variants of the syndrome with different clinical manifestationsThe most commonly reported neurological signs and symptoms were ascending motor weakness (tetraparesis and paraparesis), diminished deep tendon reflexes, sensory disturbances (paresthesia), sensory loss, and facial palsy GBS was complicated by respiratory failure in 30 cases and dysautonomia in casesGUILLAINBARRE SYNDROME JAMES W ALBERS, MD, PhD GuiIlainBarre syndrome or acute idiopathic polyradiculoneuritis is a disorder of unknown eti ology involving the peripheral nervous system Although established diagnostic criteria' are de scriptive, electrodiagnostic findings are often char acteristic and important in both establishing the




Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein In Guillain Barre Syndrome Need For Age Dependent Interpretation Hegen 21 European Journal Of Neurology Wiley Online Library



Eric Topol A Guillain Barre Syndrome In 5 Patients Who Were Infected W Covid19 T Co Zkjtake9x9 This Report From Centers From Italy Adds To The Other Central Nervous System Involvement T Co Bmppll3ava
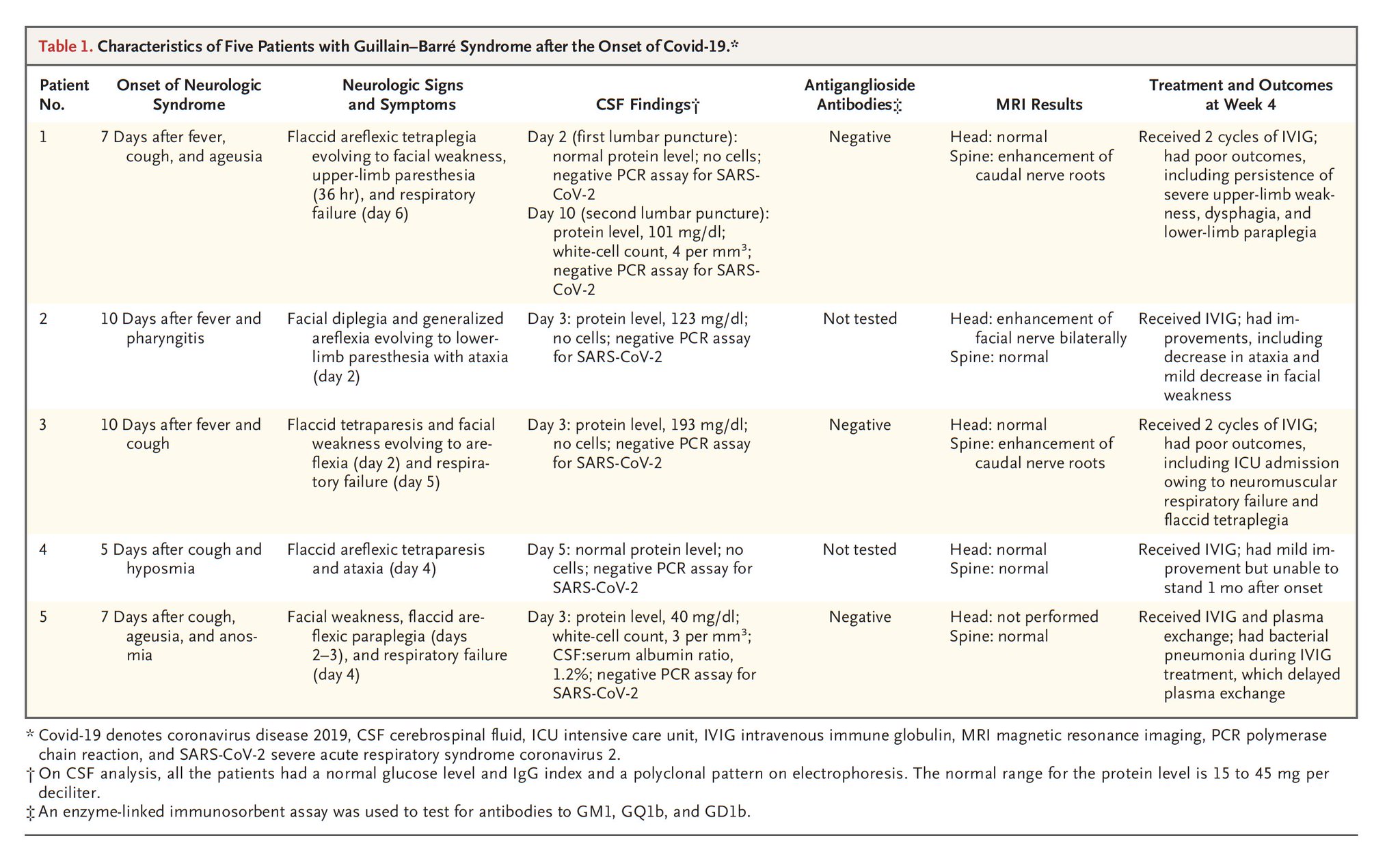
GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an acute inflammatory polyneuropathy affecting the myelinprotein sheathing and the axons themselves to various degrees Damage to these structures causes biomarkers to be released into the adjacent body fluid compartment In case of the proximal nerve roots these bi GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an acute inflammatory polyneuropathyGuillainBarré syndrome is the most common and most severe acute paralytic neuropathy, with about 100 000 people developing the disorder every year worldwide Under the umbrella term of GuillainBarré syndrome are several recognisable variants with distinct clinical and pathological features The severe, generalised manifestation of GuillainBarré syndrome with respiratory The findings were generally consistent with an axonal variant of Guillain–Barré syndrome in three patients and with a demyelinating process in two patients 1



N Neurology Org Content Neurology 61 6 3 Full Text Pdf




Clinical Variants Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Children Pediatric Neurology
A high level ofGuillainBarré syndrome may be triggered by Most a If CSF is not collected or results not available, nerve electrophysiology results must be consistent with the diagnosis GuillainBarré syndrome Tables Table 2




Age Matters Neurology Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation




Guillain Barre Syndrome Draw It To Know It
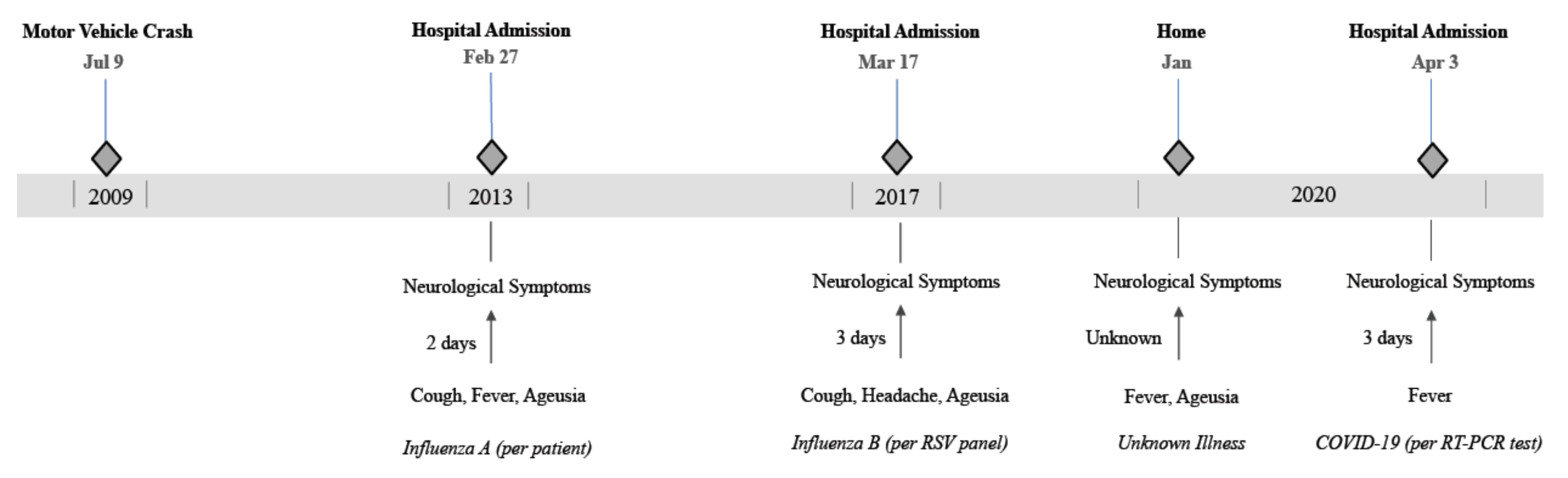
Start studying L4 CNS Infections and GuillainBarre Syndrome Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV2) mainly affects the respiratory system, but extrarespiratory involvement has also been reported, including the development of Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) 14 However, the real frequency of GBS in patients with COVID is currently unknown, and it remains unclear whether this strain ofGuillain–Barré Syndrome and JEV Infection Japanese encephalitis virus infection was confirmed in 161 patients in a northern area of Ningxia, China Signs and symptoms and electromyographic




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Elderly Clinical Electrophysiological Therapeutic And Outcome Features Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Elderly Clinical Electrophysiological Therapeutic And Outcome Features




Pdf Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome And Validation Of Brighton Criteria Semantic Scholar
Decreased or absent reflexes are seen in approximately 90% of patients Respiratory muscle weakness that may require ventilatory support can develop in 30% of patients Facial nerve paralysis can develop in up to half of the patients Autonomic 1 INTRODUCTION The diagnosis of Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS), the leading global cause of acute flaccid paralysis (Yuki & Hartung, 12), is largely based on clinical features, and supported by serological, electrodiagnostic, and immunological investigationsHowever, the manifestations of GBS are protean and include limited forms such as acute ophthalmoparesis CSF IL8 was higher in GBS (median 9 pg/mL) than in CIDP (410 pg/mL) (p< 0001) Receiver operating characteristic analyses indicated that the optimal IL




Cureus Neurological Complications Of Covid 19 Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Pfizer Covid 19 Vaccine
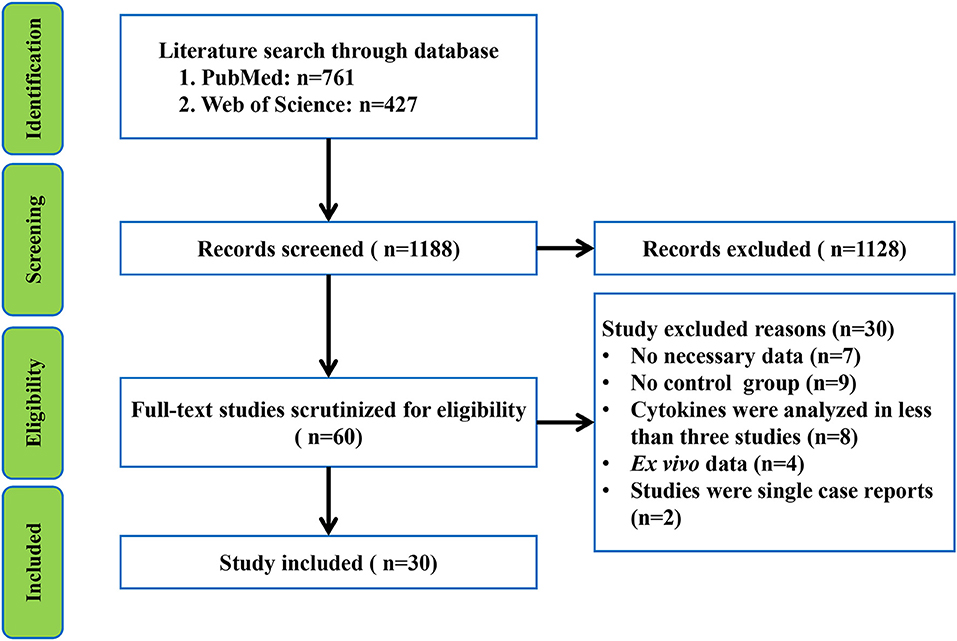



Frontiers Peripheral Blood And Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine Levels In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Neuroscience
BackgroundZika virus (ZIKV) infection has been linked to the Guillain–Barré syndrome From November 15 through March 16, clusters of cases of the Guillain–Barré syndrome were observed GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an immunemediated polyradiculoneuropathy frequently preceded by an infection with Campylobacter jejuni or nonspecific infections, and rarely by a vaccination Due to a lack of a pathognomonic finding or biomarker, its diagnosis is based on a typical constellation of clinical and paraclinical symptoms and findingsAbstract Clinical data and the serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) findings of 71 patients with GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS), 7 with Fisher syndrome and 24 with chronic inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy (CIP), were analysed Isoelectric focusing of serum and CSF together with different formulae and diagrams were applied to study bloodCSF barrier (BCB) function and
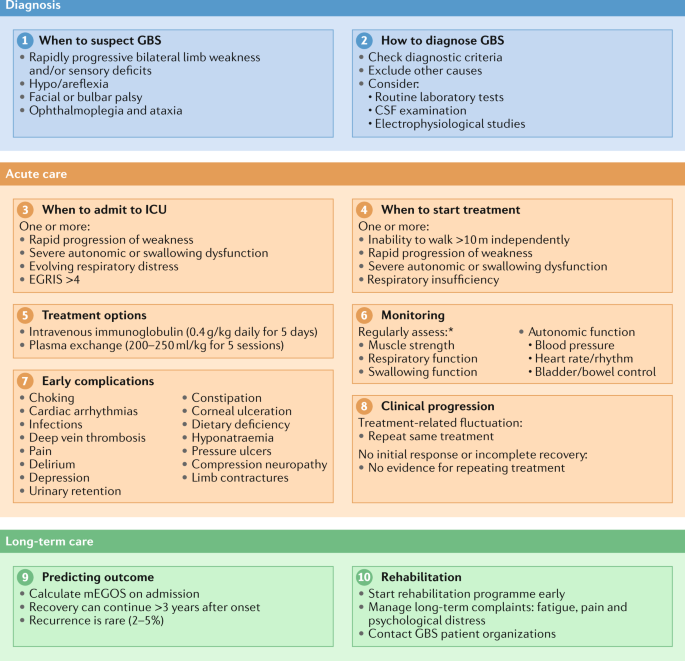



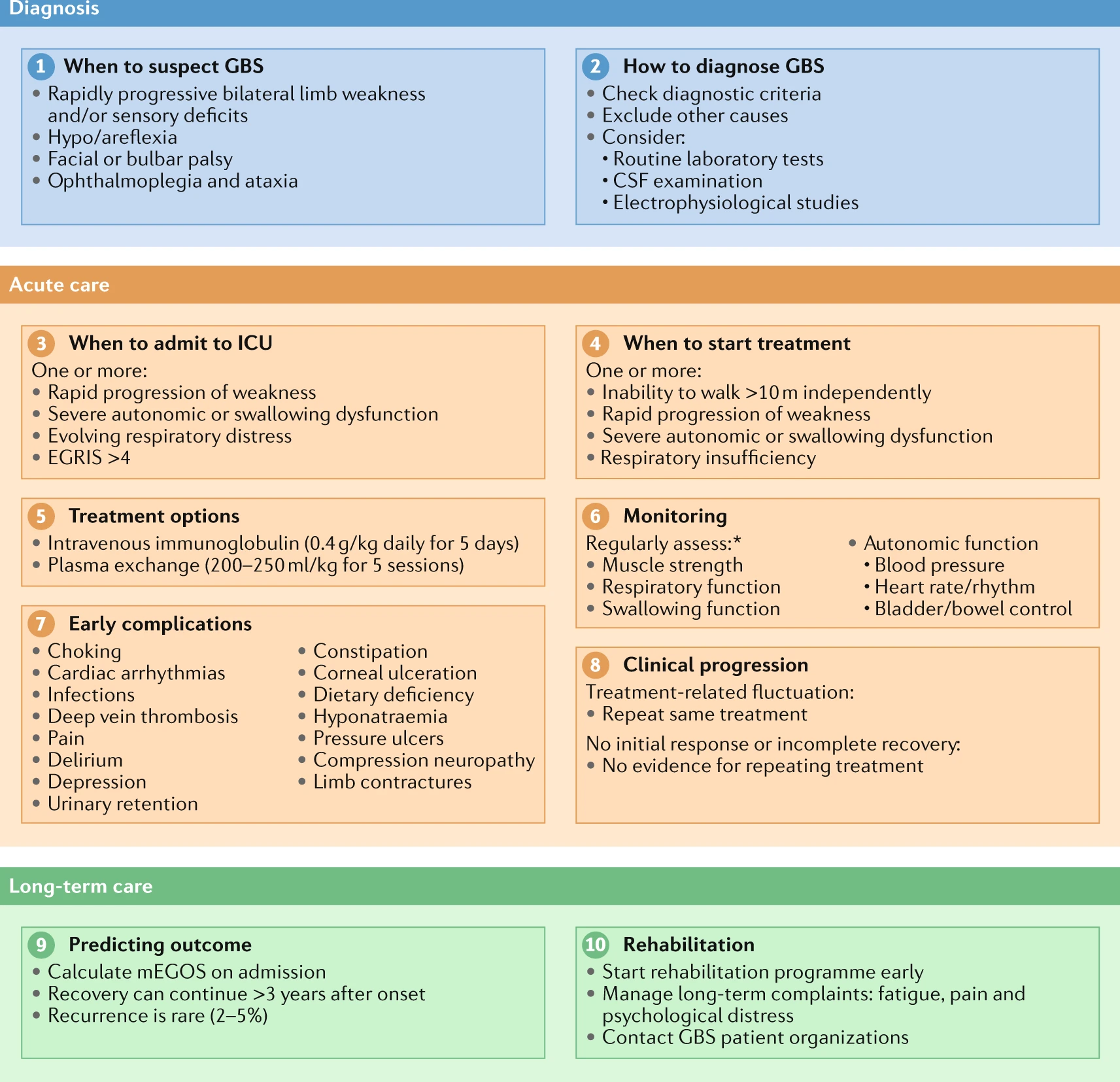
Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Nature Reviews Neurology




Guillain Barre Syndrome Mayo Clinic Proceedings
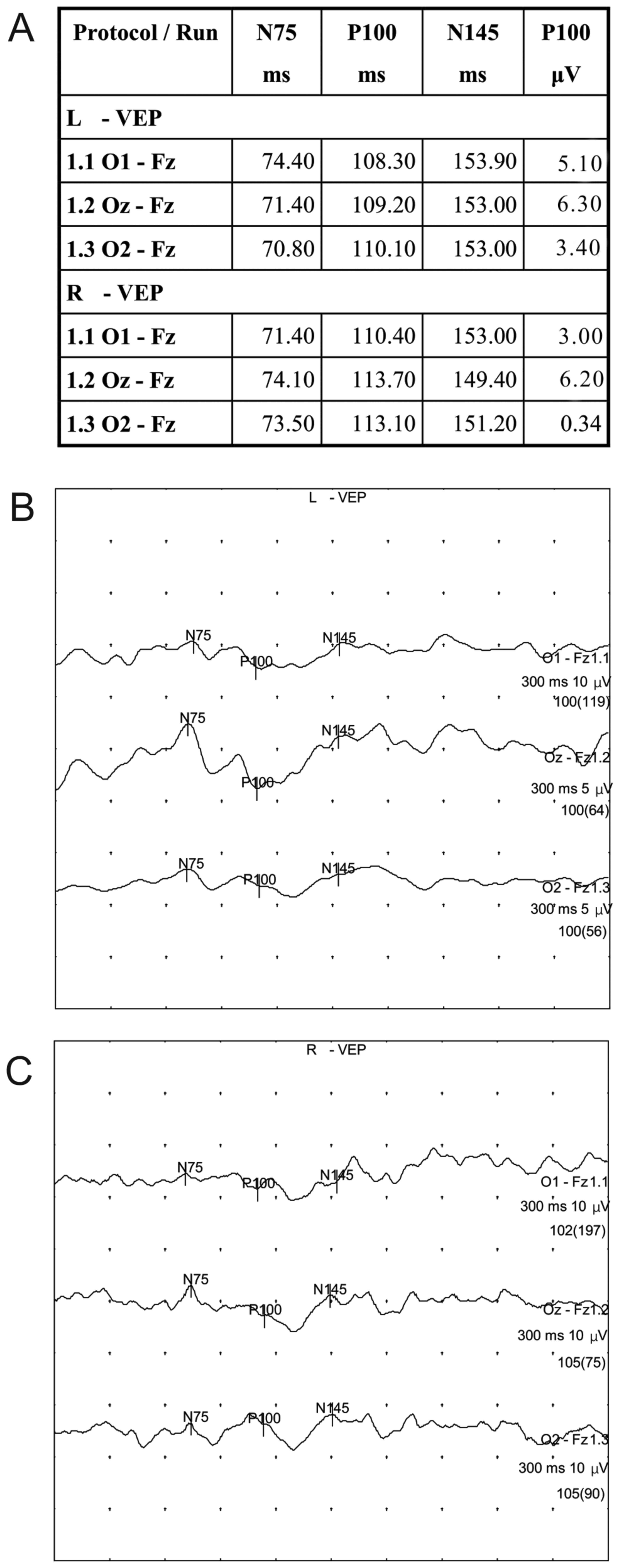



Acute Bilateral Vision Deficit As The Initial Symptom In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Case Report




Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning




Guillain Barre Syndrome Crash Medical Review Series Youtube




Neurological Associations Of Covid 19 The Lancet Neurology




Supplemental Materials For Distal Limb Weakness Phenotype Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Biomarkers Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Some Recent Progress More Still To Be Explored



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Arm Annals Of Rehabilitation Medicine




Comparison Of Tm And Gbs Download Table
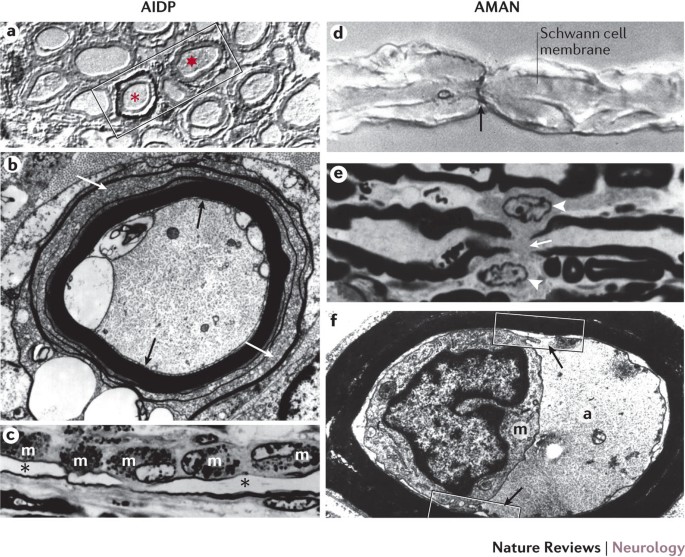



Guillain Barre Syndrome A Century Of Progress Nature Reviews Neurology




Clinical And Electrophysiological Features Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Iran Sciencedirect



Frontiers Trauma Related Guillain Barre Syndrome Systematic Review Of An Emerging Concept Neurology




Clinical Significance Of Serum And Csf Findings In The Guillain Barre Syndrome And Related Disorders Semantic Scholar



Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




Clinical And Laboratory Findings In Five Patients With Guillain Barre Download Table




Surgery And Guillain Barre Syndrome A Single Center Retrospect Ndt



Improved A Guillain Barre Syndrome Patient With Positive Pcr Test For Coronavirus In Cerebrospinal Fluid After Plasmapheresis A Case Report Jentashapir Journal Of Cellular And Molecular Biology Full Text




Findings Of Cerebrospinal Fluid During The Initial Presentation In 02 Download Scientific Diagram




Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings In The Landry Guillain Barre Strohl Syndrome Neurology




Interleukin 8 A Biomarker To Differentiate Guillain Barre Syndrome From Cidp Neurology Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation
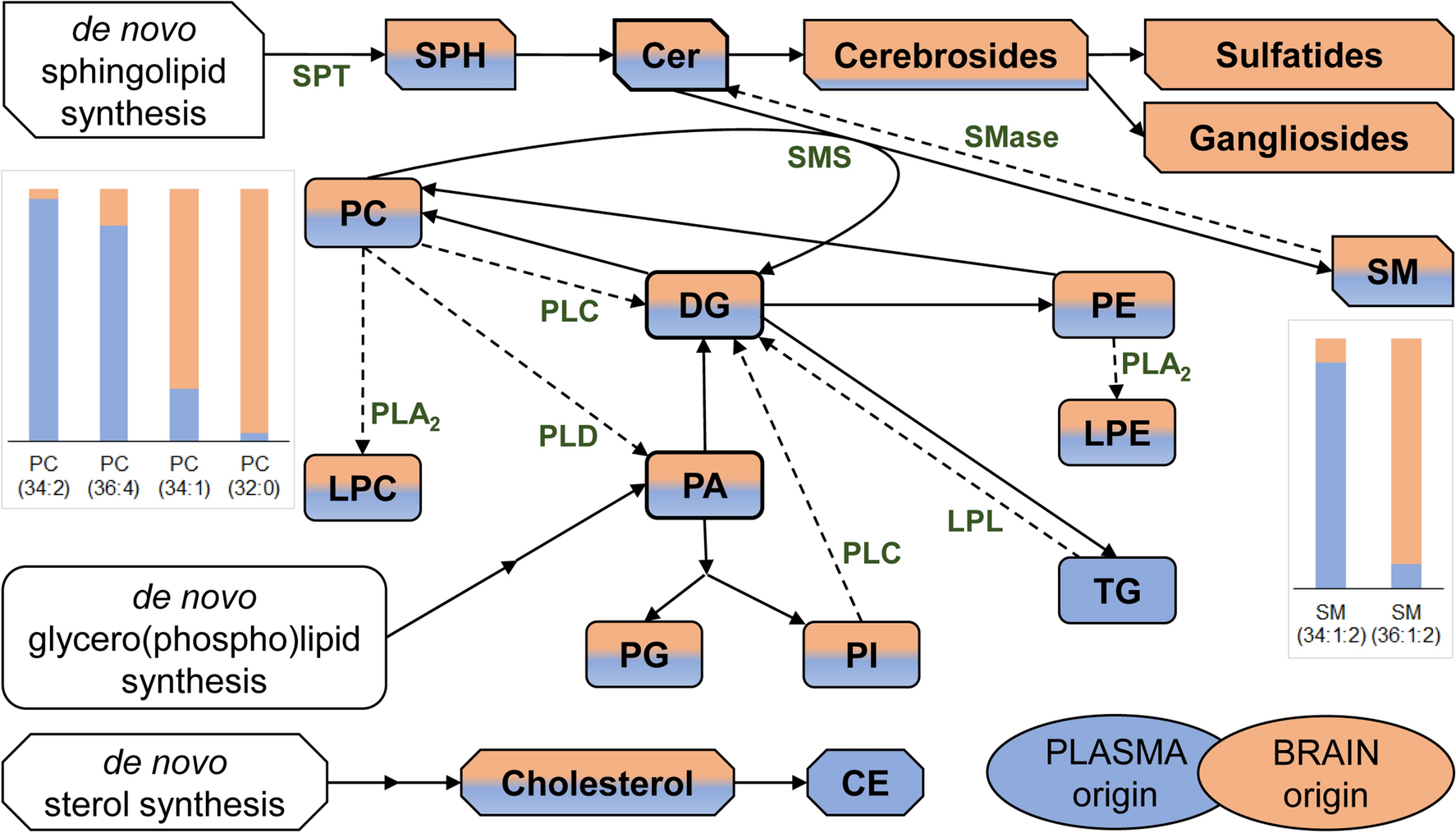



Cerebrospinal Fluid Lipidomic Biomarker Signatures Of Demyelination For Multiple Sclerosis And Guillain Barre Syndrome Scientific Reports




Review Article On Covid 19 And Guillain Barre Syndrome



Clinical Presentations As Predictors Of Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation In Guillain Barre Syndrome In An Institution With Limited Medical Resources Smj




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Zika Virus Infection In Colombia Nejm
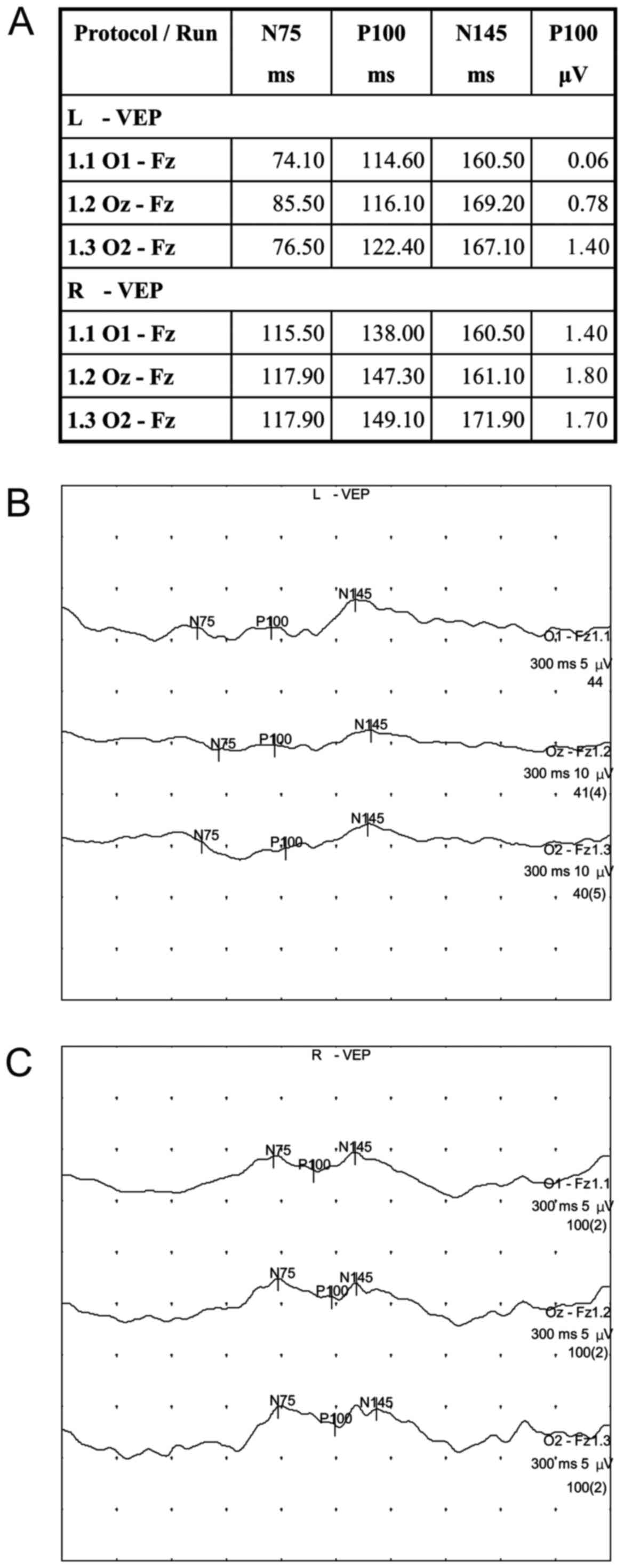



Acute Bilateral Vision Deficit As The Initial Symptom In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Case Report




Jkms Journal Of Korean Medical Science




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Pdf Early Electrodiagnostic Findings In Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar



Frontiers Sars Cov 2 Infection And Guillain Barre Syndrome A Review On Potential Pathogenic Mechanisms Immunology




Frontiers Peripheral Blood And Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine Levels In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Neuroscience
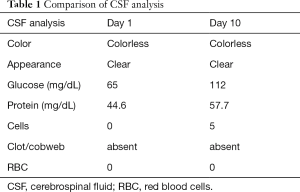



A Rare Case Of Fulminant Gbs Mimicking Brain Death With Clinical Recovery Trivedi Journal Of Emergency And Critical Care Medicine




Scielo Brasil Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Dengue Fever Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Dengue Fever



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




The Guillain Barre Syndrome Nejm




Causes Of Albuminocytological Dissociation And The Impact Of Age Adjusted Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein Reference Intervals A Retrospective Chart Review Of 2627 Samples Collected At Tertiary Care Centre Bmj Open



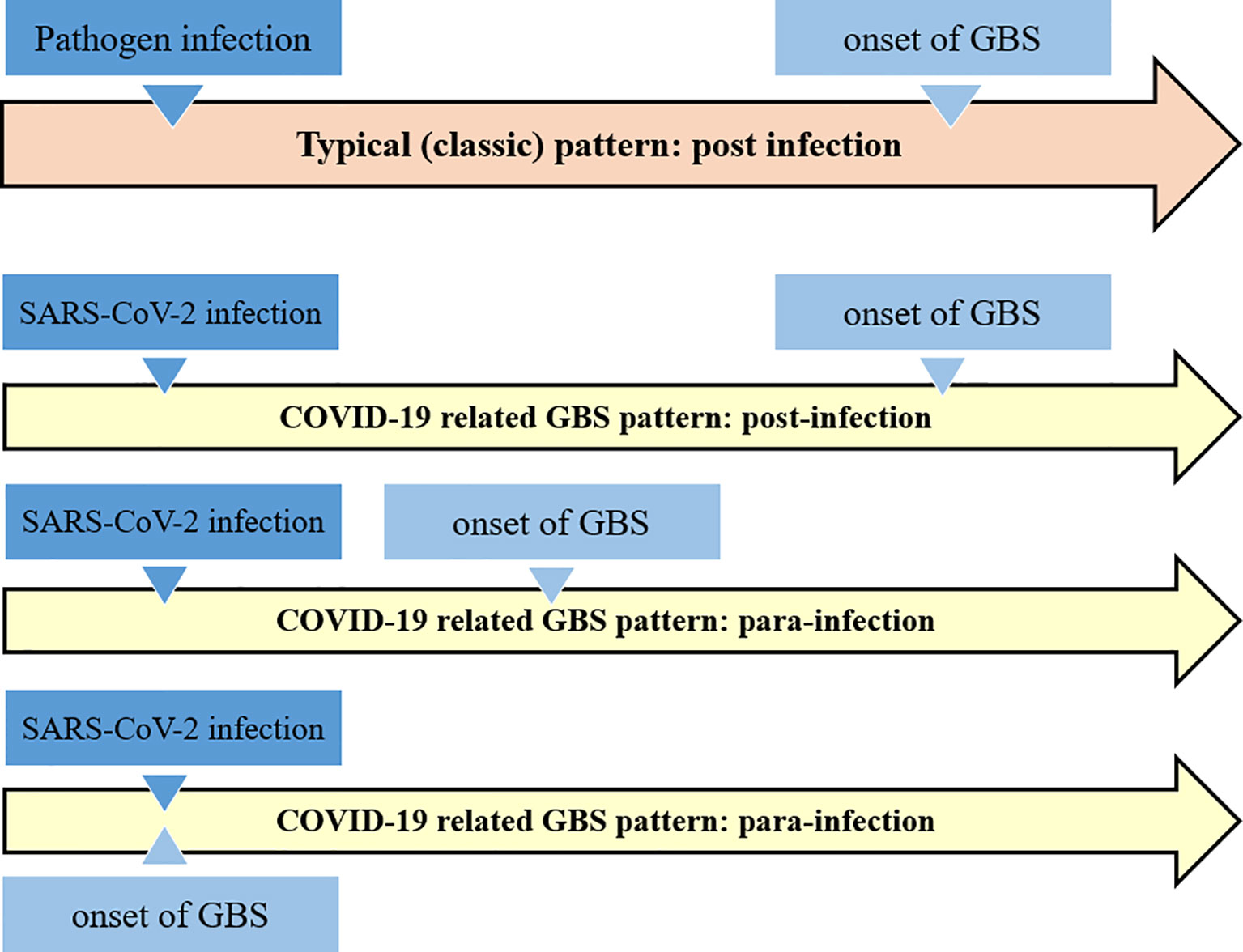
Pathogens Free Full Text Covid 19 As A Trigger Of Recurrent Guillain Barre Syndrome Html




Miller Fisher Variant Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Eyewiki



Update From The International Guillain Barre Syndrome Outcome Study Igos Gbs Cidp Foundation International



Http Scf Cpqam Fiocruz Br Merg Index Php Component Phocadownload Category 6 Publicacoes Download 45 Immunopathology Of Guillain Barre Syndrome




Prevalence And Outcomes Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Among Pediat Ndt




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician
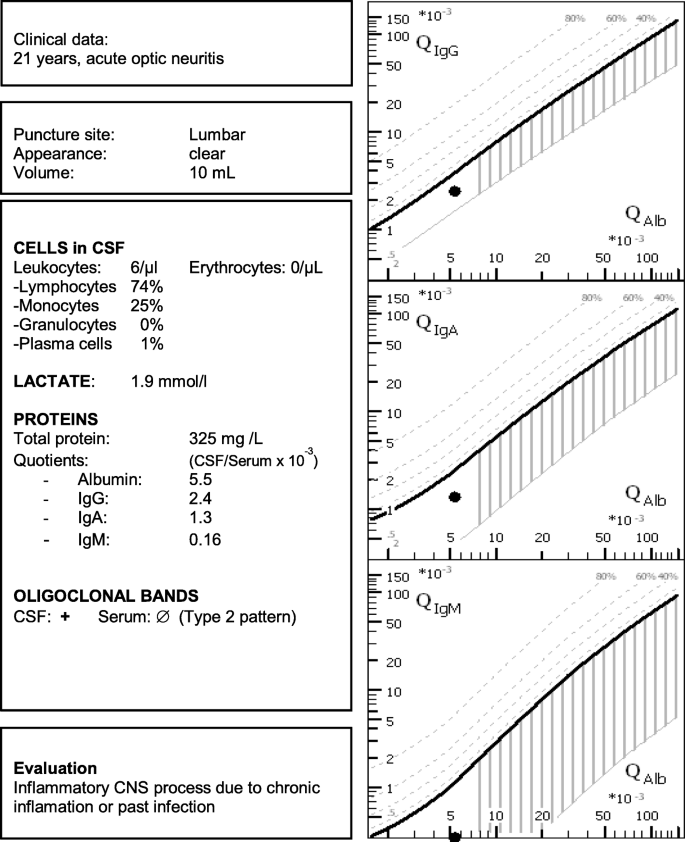



S1 Guidelines Lumbar Puncture And Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis Abridged And Translated Version Neurological Research And Practice Full Text




Causes Of Albuminocytological Dissociation And The Impact Of Age Adjusted Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein Reference Intervals A Retrospective Chart Review Of 2627 Samples Collected At Tertiary Care Centre Bmj Open
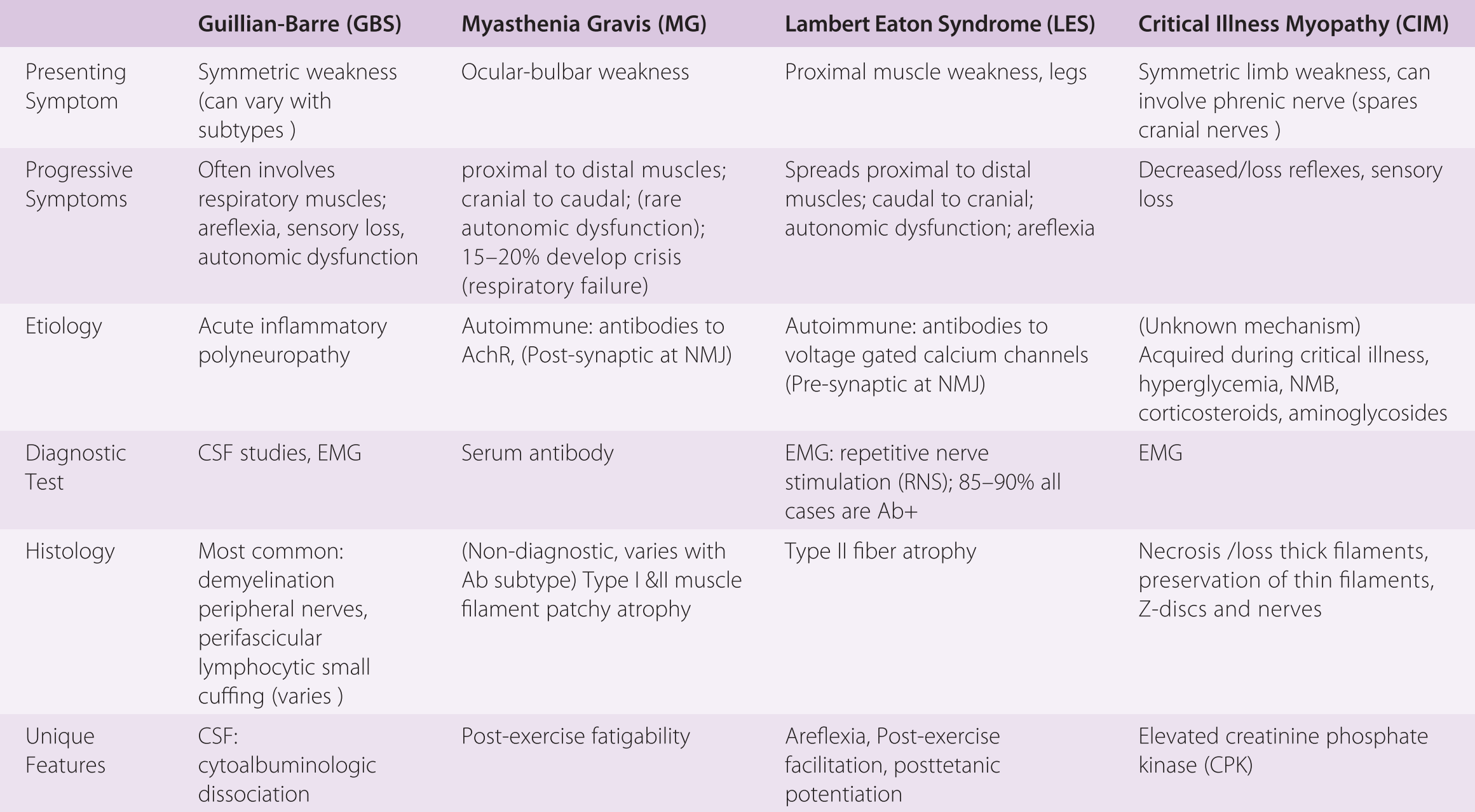



Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Sars Cov 2 Nejm




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Elderly Clinical Electrophysiological Therapeutic And Outcome Features Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Elderly Clinical Electrophysiological Therapeutic And Outcome Features



Clinical Presentations As Predictors Of Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation In Guillain Barre Syndrome In An Institution With Limited Medical Resources Smj




Scielo Brasil Oligosymptomatic Dengue Infection A Potential Cause Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Oligosymptomatic Dengue Infection A Potential Cause Of Guillain Barre Syndrome



Manifestaciones Neurologicas De La Infeccion Por El Virus Zika




Clinical Significance Of Serum And Csf Findings In The Guillain Barre Syndrome And Related Disorders Semantic Scholar




Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis Results Download Table




A 69 Year Old Woman With Double Vision And Lower Extremity Weakness Consult Qd




Pdf Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar
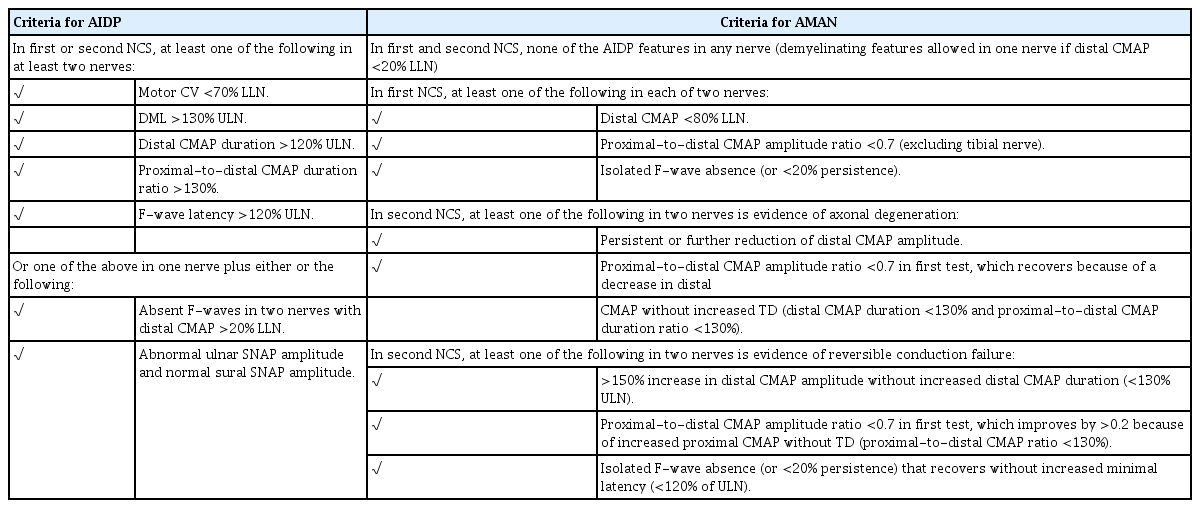



Electrognostic Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 161 1




Guillain Barre Syndrome Mimics Tham 18 Brain And Behavior Wiley Online Library




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician




Scielo Brasil Laboratorial Diagnosis Of Lymphocytic Meningitis Laboratorial Diagnosis Of Lymphocytic Meningitis




Interleukin 8 Differentiates Guillain Barre Syndrome Variant From Cidp Neurology Advisor




Surgery And Guillain Barre Syndrome A Single Center Retrospect Ndt




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet
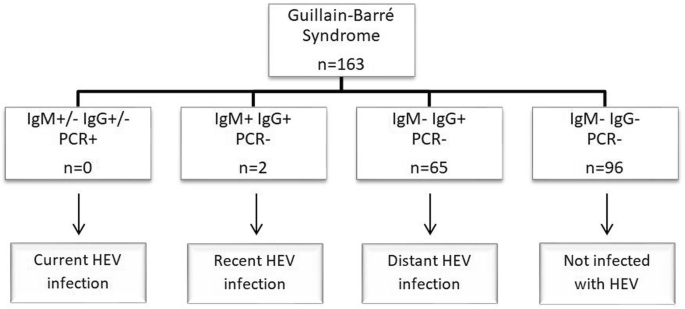



Hepatitis E Virus As A Trigger For Guillain Barre Syndrome Bmc Neurology Full Text




Nerve Conduction Studies In Guillain Barre Syndrome Influence Of Timing And Value Of Repeated Measurements Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Treatment Guidelines For Guillain Barre Syndrome Meena A K Khadilkar S V Murthy J Ann Indian Acad Neurol




Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning
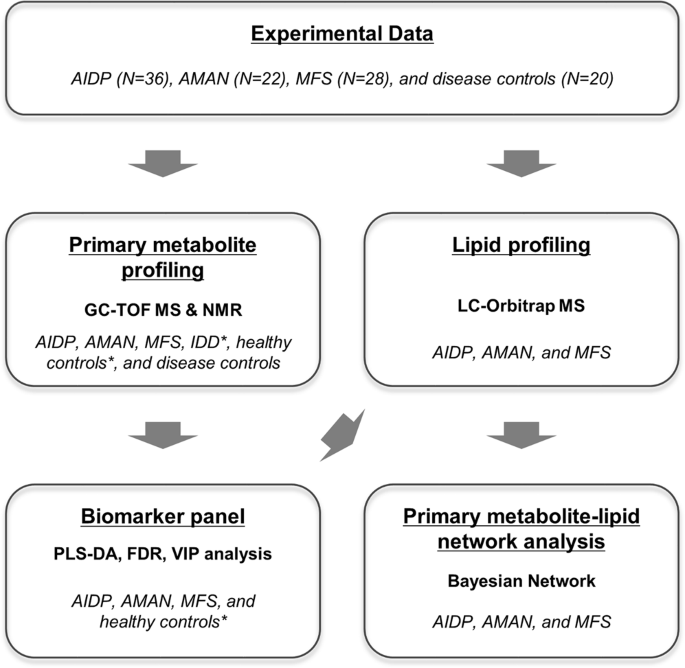



Integrative Metabolomics Reveals Unique Metabolic Traits In Guillain Barre Syndrome And Its Variants Scientific Reports



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Csf Findings In Guillain Barre Syndrome Demyelinating And Axonal Acute Inflammatory Polyneuropathies Springerlink




Arm Annals Of Rehabilitation Medicine




Laboratory Findings At Initial Presentation And Recurrence Of Download Table




Comment On Lumbar Mri Findings In Guillain Barre Syndrome The Spine Journal




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician



Www Orpha Net Data Patho Pro En Guillainbarre Frenpro4v01 Pdf
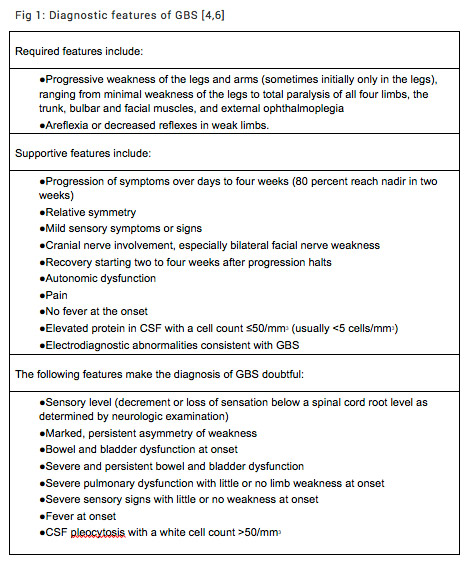



Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning



Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Emcrit Project




Surgery And Guillain Barre Syndrome A Single Center Retrospect Ndt



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿